AI and Big Data Governance: Challenges and Top Benefits
Artificial intelligence (AI) and big data share a symbiotic relationship. One of the primary challenges in implementing big data governance is ensuring data awareness and understanding across the organization. Data governance initiatives often fail when stakeholders are not aware of the importance of data governance or lack the knowledge to implement it effectively. Automation plays a pivotal role in modern data governance, significantly enhancing cost-effectiveness. By automating processes, organizations can streamline governance efforts and allocate resources more efficiently. Machine learning further advances these efforts by accelerating metadata collection and improving categorization accuracy, highlighting its critical role in optimizing data governance practices.
Also Read: How AI Is Transforming Big Data?
AI relies heavily on vast datasets for enhancing model training, enabling more precise predictions. Concurrently, big data leverages AI tools to bolster its analytical capabilities. AI’s effectiveness hinges on data availability. Without sufficient data, AI functions merely as a theoretical concept. This interplay becomes increasingly crucial as data accessibility expands, facilitating machine learning and iterative processes that drive improved accuracy and operational efficiency autonomously.
A recent report from Drexel University’s LeBow Center for Business Analytics reveals that 77% of data and analytics professionals prioritize data-driven decision-making within their data programs. However, less than half of survey respondents express high or very high levels of trust in their data. This lack of confidence is largely attributed to poor data quality, which not only obstructs the success of data programs but also undermines data integration efforts and compromises data integrity, presenting significant challenges for big data governance.
Understanding Big Data Governance
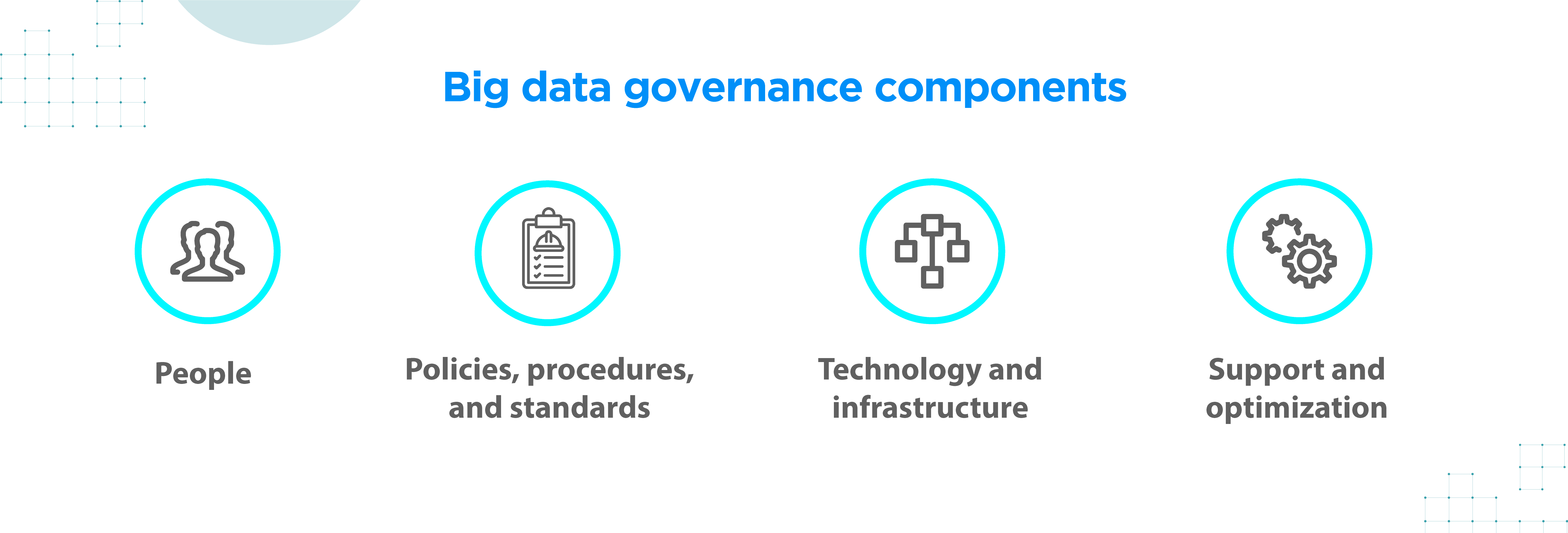
Big data governance refers to the management framework implemented within an organization to ensure the proper handling, integrity, usability, and security of big data sets. This framework includes policies, procedures, and standards that govern data access, data quality, compliance with data-related regulations, and data protection.
![]() AIGA AI Governance Framework
AIGA AI Governance Framework
The AIGA AI Governance and Auditing, led by the University of Turku in Finland, collaborates with academic and industry partners, akin to Google, to offer guidance on the responsible development and deployment of AI.
The AIGA AI Governance Framework serves as a practical manual for organizations aiming to implement ethical and responsible AI systems. Its primary objectives include:
- Providing a systematic approach to AI governance, covering the entire lifecycle of AI systems—from initial design to testing, deployment, monitoring, and updates. It integrates governance tasks with different stages of the AI lifecycle.
- Assisting organizations in meeting forthcoming AI regulations, such as the European Union’s AI Act, which mandates legal standards for high-risk AI applications. This framework is particularly relevant for companies developing proprietary AI systems for sensitive domains.
- Equipping organizational decision-makers with a structured framework to address critical issues regarding the ethical use of AI technology, including transparency, fairness, accountability, and safety.
- Remaining “value-agnostic,” thereby not endorsing any specific ethical doctrine. Instead, it emphasizes practices that foster trustworthy and conscientious AI systems across diverse operational contexts.
Ethical AI and Big Data Governance: A Critical Intersection
At the core of the discussion, there is an overlaying of ethical AI, data policies, and current data governance. Besides mere algorithmic technical acquaintance, ethical AI encompasses efforts to imbue fairness, transparency, and accountability in the conduction and implementation of AI. Conversely, data governance avails the scaffold for dealing responsibly in the management, protection, and usage of data assets.
Fairness ensures that AI systems do not reflect bias or result in discrimination. This is the principle that will assure stakeholders about the operations of the AI algorithms. Accountability creates liability for developers and operators in AI systems’ decisions and results. These principles make AI applications greater in lowering ethical risks and increasing trust from users and society.
It addresses the interplay between a concern for ethics in AI and data governance by identifying a series of challenges and opportunities. It emphasizes the requirement to establish a basis for a culture of conscientiousness and responsibility concerning ethical AI. Companies engaging with such matters of ethics will be able to maximize AI transformation and guard individual rights and aspirations.
Also Read: The Rise of AI in Data Collection: Implications and Opportunities for Businesses
The Role of AI in Big Data Governance
Organizations are nowadays using AI more and more to strengthen their data analytics ability and maintain an advantage in the market. When AI is combined with data governance rules, companies can maximize the ROI by measuring ineffective practices and boosting successful strategies:.
Their use is different in different organizational departments for varied data sources that are used in their respective industries—for example, sales departments that analyze consumer trends. This use has been quite populous with the use of predictive analytics, which increases operational efficiency.
The manufacturing departments in organizations base their investment in AI on analytics to meet their industry needs, targeting the betterment of productive processes, when hardly anything else is. Root causes for quality issues are identified, and then management is equipped to make decisions, and just maybe, those issues are prevented through predictive maintenance strategies.
AI is important for the detection of anomalies and cybersecurity. Machine learning makes AI perform the detection and response of threats timely, especially those concerning data breaches. This proactive approach ensures data integrity and compliance through continuous monitoring and rapid response capabilities.
The democratization of data governance is greatly increased, with AI providing secure data access and not intercepted by cybercriminals—meaning sophisticated tactics such as Man-In-The-Middle or ransomware. By automating privacy, compliance, and security measures, AI acts as a 24/7 safeguard against cyber threats, thus enhancing data protection.
Moreover, AI also enables the automated discovery of processes, while being able to analyze behavioral data and develop digital records with ease, hence effectively streamlining processes for data management.
Key Challenges in AI and Big Data Governance
Quality and Bias Concerns
AI systems heavily rely on extensive datasets for learning and operational tasks. However, ensuring data accuracy and fairness poses challenges when dealing with incomplete, outdated, inconsistent, or biased data. Organizations must establish stringent data standards, validate sources rigorously, and continually monitor and audit data quality throughout the AI lifecycle to mitigate these issues effectively.
Security and Privacy Risks
The processing of sensitive data by AI systems, such as health records or financial information, exposes organizations to significant risks like breaches and misuse. Securing data through robust encryption, access controls, and anonymization techniques is crucial. Moreover, compliance with data protection regulations and ethical principles is essential to safeguard against unauthorized access and ensure data privacy.
Interoperability Complexity
Integrating diverse data types (structured, unstructured, streaming) from various sources (internal, external, cloud-based) presents significant challenges in data consistency and compatibility. Adopting standardized data models, schemas, and formats, along with leveraging integration tools and platforms, helps organizations achieve seamless data exchange and interoperability across systems.
Cultivating a Data-Driven Culture
Effective utilization of AI requires a workforce equipped with strong data literacy skills and a supportive data-driven organizational culture. Enhancing data literacy involves enabling employees to understand, analyze, and effectively utilize data. Fostering a data-driven culture encourages informed decision-making and innovation. Organizations should invest in comprehensive data education, training, and collaborative initiatives to build trust and maximize the adoption of AI technologies among stakeholders.
Benefits of AI-Powered Big Data Governance
Improve Data Quality
Data quality is fundamental to any effective data strategy. AI enhances data quality by automating error detection and correction within datasets, thereby reducing inconsistencies and inaccuracies. AI algorithms also standardize data structures, facilitating easier comparison and analysis while uncovering hidden trends and patterns.
Automate Data Compliance
In today’s landscape of escalating cyber threats, maintaining data compliance is crucial. AI plays a pivotal role in ensuring continuous compliance by monitoring data flows in real-time. It detects anomalies, unauthorized access attempts, and potential violations of data regulations, triggering alerts and recommendations for corrective actions. Additionally, AI automates the classification and labeling of sensitive data and generates compliance reports, thereby reducing administrative burdens.
Strengthen Data Security
AI enhances data security by proactively analyzing data access patterns to detect suspicious activities such as intrusions or unauthorized access attempts. Leveraging machine-learning-based malware detection systems, AI identifies and mitigates both known and unknown threats by analyzing behavioral patterns. Moreover, AI automates security patch management and monitors adherence to security policies, bolstering overall cybersecurity measures.
Democratize Data
Central to effective data strategy is fostering a data-driven culture within organizations. AI facilitates this by simplifying data access and analysis. AI-powered search engines swiftly extract relevant information from extensive datasets, enabling employees to efficiently retrieve necessary data. Furthermore, AI automates data aggregation and presentation through interactive dashboards, enhancing data accessibility and facilitating seamless information sharing across teams.

 AIGA AI Governance Framework
AIGA AI Governance Framework






Comments are closed.