Top 15 AI Trends In 5G Technology
The 5G revolution began in 2016. In the last seven years, this technology has been meeting the growing needs of many different sectors, from storage facilities and ports to factories and smart cities. With technologies like cloud and edge computing, and IoT maturing at a fast pace, 5G is anticipated to play a vital part in Industry 4.0. 60% of communications services providers (CSPs) would provide commercialized multi-regional 5G services in 2024, almost matching the adoption rates of LTE and 4G. The 5G industry has created 22.8 million jobs so far. PWC’s 5G technology report has forecasted a $1.3 trillion addition to the global GDP by 2030. For companies exploring new opportunities in 2024, kick-starting with 5G technology could amplify the benefits of working with new-gen digitally connected technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, Web 3.0, and the internet of things (IoT).
Table: Wireless Infrastructure Revenue Forecast, Worldwide, 2018-2021 (Millions of Dollars)
| Segment | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 |
| 5G
2G 3G LTE and 4G Small Cells Mobile Core |
612.9
1,503.1 5,578.4 20,454.7 4,785.6 4,599.0 |
2,211.4
697.5 3,694.0 19,322.4 5,378.4 4,621.0 |
4,176.0
406.5 2,464.3 18,278.2 5,858.1 4,787.3 |
6,805.6
285.2 1,558.0 16,352.7 6,473.1 5,009.5 |
| Total | 37,533.6 | 35,924.7 | 35,970.5 | 36,484.1 |
5G is driving global growth with $13.1 Trillion global economic output and 22.8 Million new jobs created
along with $265B global 5G CAPEX and R&D annually over the next 15 years.
What is “5G”?
5G refers to the fifth generation of mobile networks. After 1G,2G, 3G, and 4G networks, this is the next generation of wireless technology. With the advent of 5G, a new type of network is possible, one that may theoretically link up any machines, objects, and gadgets.
According to Ericsson’s “5G: The Next Wave” report, 5G adoption is inflation-resilient. 510 million smartphone users could upgrade to a 5G subscription; 80% of 5G users not returning to 4G usage. Despite the lightning speed of adoption, only 70% of 5G users are satisfied with the service availability and customer experience. Increasing 5G connectivity coverage can quadruple customer service compared to the existing 4G infrastructure.

Multi-gigabit per second (Gbps) peak data rates, ultra-low latency, enhanced dependability, huge network capacity, more availability, and a more consistent user experience are all goals of 5G wireless technology. New user experiences and industry connections are made possible by increased performance and efficiency.
Below is a survey by Deloitte depicting 5G capability.
What fundamental technologies underpin 5G networks?
5G is based on OFDM (Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing), a way of modulating a digital transmission across several distinct channels to decrease interference. 5G employs the 5G NR air interface and the OFDM underlying technology. Sub-6 GHz and mmWave are only two examples of the higher bandwidth technologies used by 5G. 5G OFDM is a mobile networking standard that builds on the success of 4G LTE. However, the new 5G NR air interface may further augment OFDM to give a considerably higher degree of flexibility and scalability.
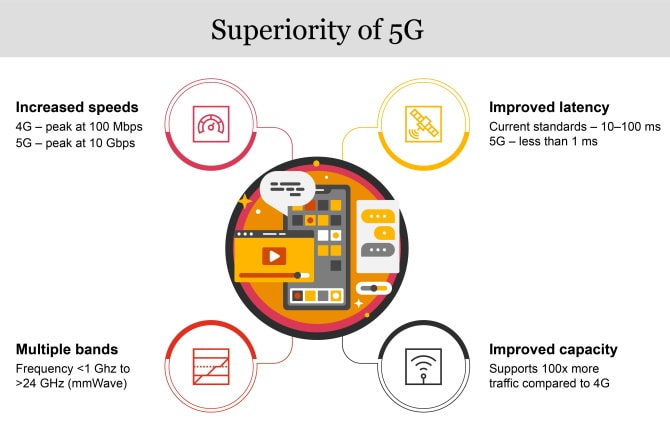
5G will increase bandwidth by using more of the available spectrum, from the current sub-3 GHz used by 4G up to 100 GHz and beyond. Both sub-6 GHz and mmWave frequencies can support 5G’s operation, giving users access to the technology’s extraordinary capacity, multi-Gbps speed, and low latency. In addition to improving upon the mobile broadband services offered created can branch out into uncharted service territories, such as providing mission-critical communications and linking the vast Internet of Things. This is made possible by many cutting-edge approaches to designing the air interface for 5G NR, such as a novel self-contained TDD subframe layout.
The 5G Transition
- First generation (1G): This technology was established in the 1980s and was the standard used for analog telephony.
- Second-generation (2G) networks typically take 40 minutes to download a 30 MB file.
It followed the 1G standard and made it possible for digital communications to be sent across cellular networks in the 1990s. - Third generation (3G); a 30 MB file typically takes 1 minute to download)
This technology, first seen in the 2000s, is often credited for ushering in the era of widespread smartphone internet access. - Fourth-generation (4G) networks allow users to download a 30 MB file in around 8 seconds. Faster mobile data connectivity, via 4G Long Term Evolution (LTE), emerged in the next decade.
Read the Latest blog from us: AI And Cloud- The Perfect Match
5G services
Increased mobile broadband, vital communications, and the vast Internet of Things are the three primary use cases for 5G networks. One of 5G’s defining features is its potential to enable future services that are now hypothetical.
Faster Mobile Internet
The faster, more consistent data rates, reduced latency, and cheaper cost-per-bit of 5G mobile technology will not only make our devices better but will also bring in new immersive experiences like VR and AR.
Critical communications
With ultra-reliable, accessible, low-latency networks, 5G will enable new services that can alter sectors, such as remote control of key infrastructure, automobiles, and medical operations.
Cheap connection options
With the capacity to scale down data speeds, power, and mobility, Massive IoT 5G aims to link a large number of embedded sensors in nearly every object in a seamless manner, all while delivering incredibly slim and cheap connection options.
Read the Latest blog from us: Risks Of IT Integration
Here are The Top 15 key trends in the intersection of AI and 5G technology:


There will be exponential growth in the amount of data produced by 5G networks. Data scientists will be in short supply in the United States alone by the time the year 2030 rolls around, according to studies. The sheer volume of information that 5G can ingest is overwhelming for human beings. Artificial intelligence (AI) is a potential solution for closing this gap.
- Network Optimization and Management: AI is being used to optimize 5G networks, automatically adjusting network parameters to improve efficiency, reduce latency, and enhance overall network performance. This includes intelligent traffic routing, load balancing, and spectrum management.
- Edge Computing: AI-driven edge computing in 5G networks allows faster data processing and real-time decision-making. This is crucial for applications like autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and IoT devices that require low latency and high bandwidth.
- Network Security: AI enhances security in 5G networks by continuously monitoring network traffic for anomalies and potential threats. It can quickly identify and mitigate security breaches and DDoS attacks.
- Network Slicing: AI enables dynamic network slicing, allowing operators to create virtualized network segments tailored to specific applications or services. This flexibility is essential for providing the diverse connectivity needs of different use cases.
- Quality of Service (QoS) Improvements: AI-driven analytics can optimize QoS by monitoring network performance in real-time and dynamically allocating resources to ensure consistent and reliable service for applications and devices.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI is used to predict and prevent network equipment failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs for 5G infrastructure.
- AI-Powered IoT and Smart Devices: 5G enables the proliferation of IoT devices. AI helps manage and analyze the vast amounts of data generated by these devices, improving their functionality and usefulness.
- Network Planning and Design: AI assists in the planning and design of 5G networks, taking into account factors like coverage, capacity, and user demand to optimize network deployment.
- Network Synchronization: AI ensures precise synchronization and timing across 5G networks, which is crucial for applications like financial transactions and critical infrastructure.
- Energy Efficiency: AI can help reduce energy consumption in 5G networks by optimizing the use of resources and minimizing power consumption during low-demand periods.
- AI-Enhanced User Experience: AI-driven analytics and personalization improve the user experience by understanding individual preferences and adapting network services accordingly.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): 5G combined with AI enables immersive AR and VR experiences by providing the high bandwidth and low latency necessary for real-time, high-quality content delivery.
- Telemedicine and Remote Healthcare: 5G and AI enable remote patient monitoring, telemedicine, and surgical procedures, expanding healthcare services to remote areas and enhancing patient care.
- AI-Powered Content Delivery: Content providers use AI to optimize content delivery, ensuring that video streaming, gaming, and other services work seamlessly on 5G networks.
- Regulatory Considerations: Policymakers are focusing on regulatory frameworks that address the convergence of AI and 5G technology, balancing innovation with privacy, security, and ethical concerns.
The integration of AI and 5G technology is expected to revolutionize various industries and pave the way for transformative applications and services. As both technologies continue to advance, they will complement each other to provide faster, more reliable, and more intelligent network solutions.
Future Predictions for AI and 5G
The advent of 5G and artificial intelligence will revolutionize the 22nd century. The effects of both technologies will be substantial, but the integration of both might lead to revolutionary shifts in our culture.
By enhancing edge computing, 5G will speed up the development of AI applications and make them more accessible. In turn, AI will handle complicated 5G networks and enable us to profit from the technology to the maximum degree.
It is crucial to consider potential vulnerabilities, such as cyber-attacks and privacy problems while utilizing both technologies. A virtual private network (VPN) may protect sensitive information while antivirus software can protect from malware.
Read: AI and Machine Learning Are Changing Business Forever
[To share your insights with us, please write to sghosh@martechseries.com]


Comments are closed.