10 AI ML In IT Security Trends To Look Out For In 2024
Remember? Last year, through a concerted effort by Microsoft, ESET, Black Lotus Labs, Palo Alto Networks, and HealthISAC, the ZLoader botnet was shut down and its malware stopped from spreading.
Remember? Through a new partnership with IBM Security, ASUS is now able to offer their enterprise customers the QRadar Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solution, giving their customers access to these capabilities.
AI-based cybersecurity has several advantages, such as improved visibility that reveals security weaknesses and enhanced identity management that prevents unauthorized individuals from accessing sensitive data and networks.
AI-driven cybersecurity solutions save time and improve the accuracy of risk assessments because of their robust analytic capabilities. They also help IT and security teams save time and effort by automating the detection and response to threats, providing them with the information they need to respond swiftly and precisely to cyber assaults.
Read 10 AI In Manufacturing Trends To Look Out For In 2024
So, What Exactly Is Artificial Intelligence Safety?
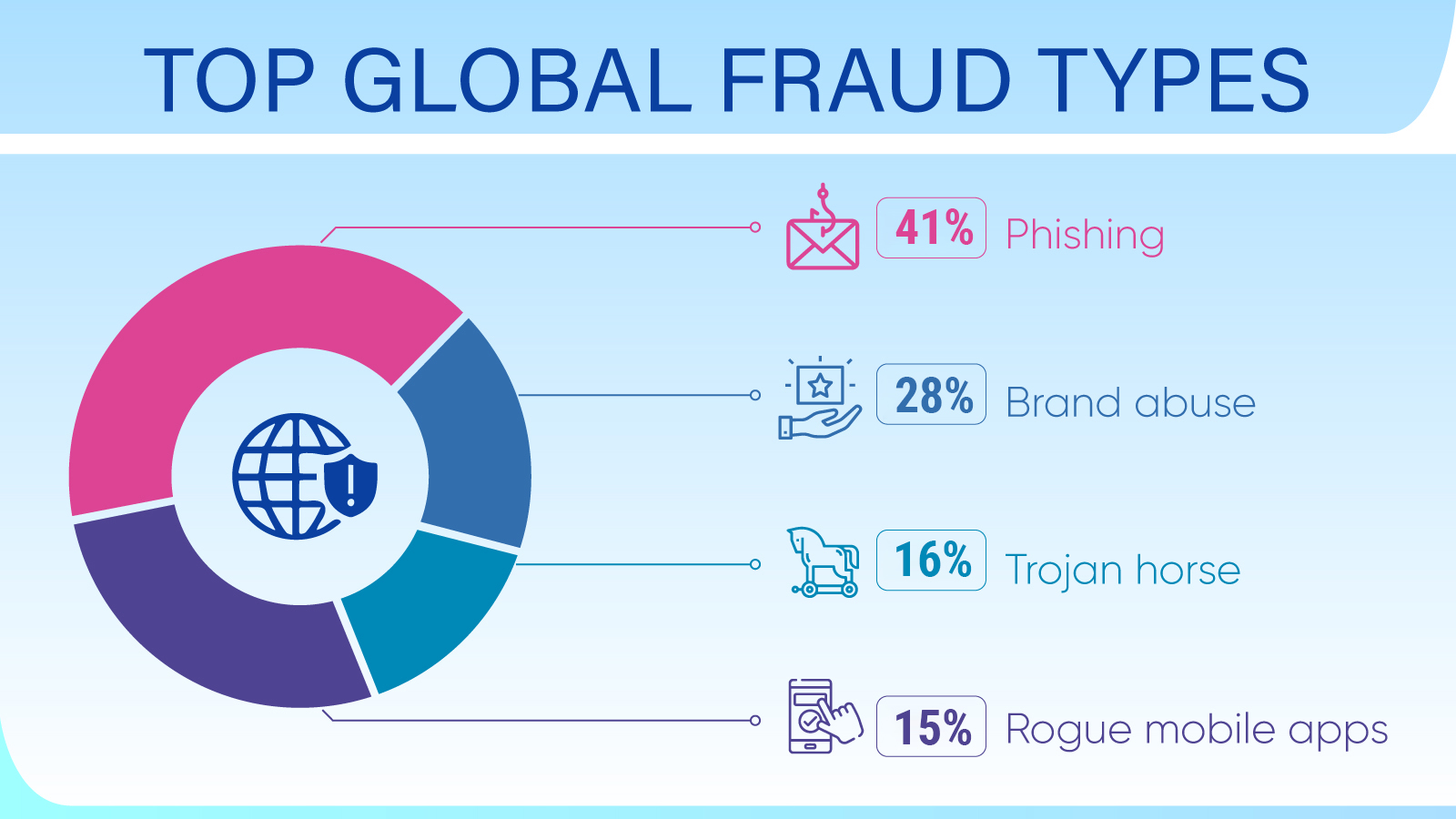
71.1 million people fall victim to cyber crimes yearly.
Cybersecurity is only one field that has benefited greatly from the advent of AI. AI security solutions have developed as strong tools for recognizing and mitigating possible dangers in today’s digital ecosystem.
 AI can analyze massive volumes of data, spot suspicious activities, and better defend businesses from cyberattacks by employing machine learning algorithms and deep learning techniques. In this post, we will examine what artificial intelligence security is, its most prevalent uses, the benefits it provides, and the most important factors to keep in mind when comparing AI cybersecurity providers.
AI can analyze massive volumes of data, spot suspicious activities, and better defend businesses from cyberattacks by employing machine learning algorithms and deep learning techniques. In this post, we will examine what artificial intelligence security is, its most prevalent uses, the benefits it provides, and the most important factors to keep in mind when comparing AI cybersecurity providers.
Advanced AI cybersecurity solutions can calculate and analyze enormous datasets, which allows them to discover activity patterns that may signal hostile action. In this way, AI simulates the ability of its human counterparts to spot potential dangers. Automation, triage, collecting alerts, sifting through alerts, automating reactions, and more are all possible thanks to AI’s use in cybersecurity. AI is commonly used to supplement the initial level of analyst work.
Read: Top 15 AI Trends In 5G Technology
Let’s Hear From an Industry Expert:
 Use of AI by Threat Actors will Drive Media Stories. Still, Not Actual Threat Actors: The use of AI by cyber criminals to enhance their attacks will continue to inspire authors more than those conducting cyber attacks for one reason: bad guys don’t need to change what they’re doing one iota to achieve success. Until the cyber security community can stop the primary attack vectors bad actors used in 2023, 2022, 2021, etc., to increase ransomware payouts and incidences of successful breaches continually, cybercriminals have no incentive to leverage AI or any other new technology for that matter, to achieve their objectives. Necessity may be the mother of invention, but where’s the evidence of necessity for bad actors?
Use of AI by Threat Actors will Drive Media Stories. Still, Not Actual Threat Actors: The use of AI by cyber criminals to enhance their attacks will continue to inspire authors more than those conducting cyber attacks for one reason: bad guys don’t need to change what they’re doing one iota to achieve success. Until the cyber security community can stop the primary attack vectors bad actors used in 2023, 2022, 2021, etc., to increase ransomware payouts and incidences of successful breaches continually, cybercriminals have no incentive to leverage AI or any other new technology for that matter, to achieve their objectives. Necessity may be the mother of invention, but where’s the evidence of necessity for bad actors?Gabriella Bussien CEO of tech-first financial crime prevention organization Trapets, a Nordic market leader since 2000, has some insights.

Top Companies in This Domain
- Crowdstrike
- Cybereason
- SparkCognition
- Tessian
- Palo Alto Networks
- Check Point Software Technologies
- Darktrace
- Fortinet
- Anomali
- Vectra AI
New: 10 AI ML In Personal Healthcare Trends To Look Out For In 2024
Let’s Understand Some Numbers
The average cost of a data breach to small businesses can range from $120,000 to $1.24 million.
Before getting into the precise sorts of cyber assaults, you need to understand how much data is involved. In 2025, the total amount of information created by humans will be 175 zettabytes (175 followed by 21 zeros). Streaming media, dating applications, and medical records are all examples of this type of data. Securing this information is crucial.
Attacks on the supply chain have become a major issue in cybersecurity during the past few years. Cyber catastrophes, such as the breach at software management provider SolarWinds and Log4j in the open source realm, put enterprises throughout the globe at risk. By 2025, 45% of global enterprises, according to Gartner, will be affected by a supply chain assault.
As technical attacks grow increasingly hard, attackers are targeting human nature. The substantial advancements in cyber protection are sometimes overshadowed by the attention paid to cybersecurity accidents.
Read: 10 AI In Energy Management Trends To Look Out For In 2024
This is because hackers are continually looking for new methods to get beyond defenses, while security experts are always adapting to new forms of cyber assault. While it’s important to acknowledge where attackers succeed, it’s also important to acknowledge where defenders succeed in making things more difficult for attackers.
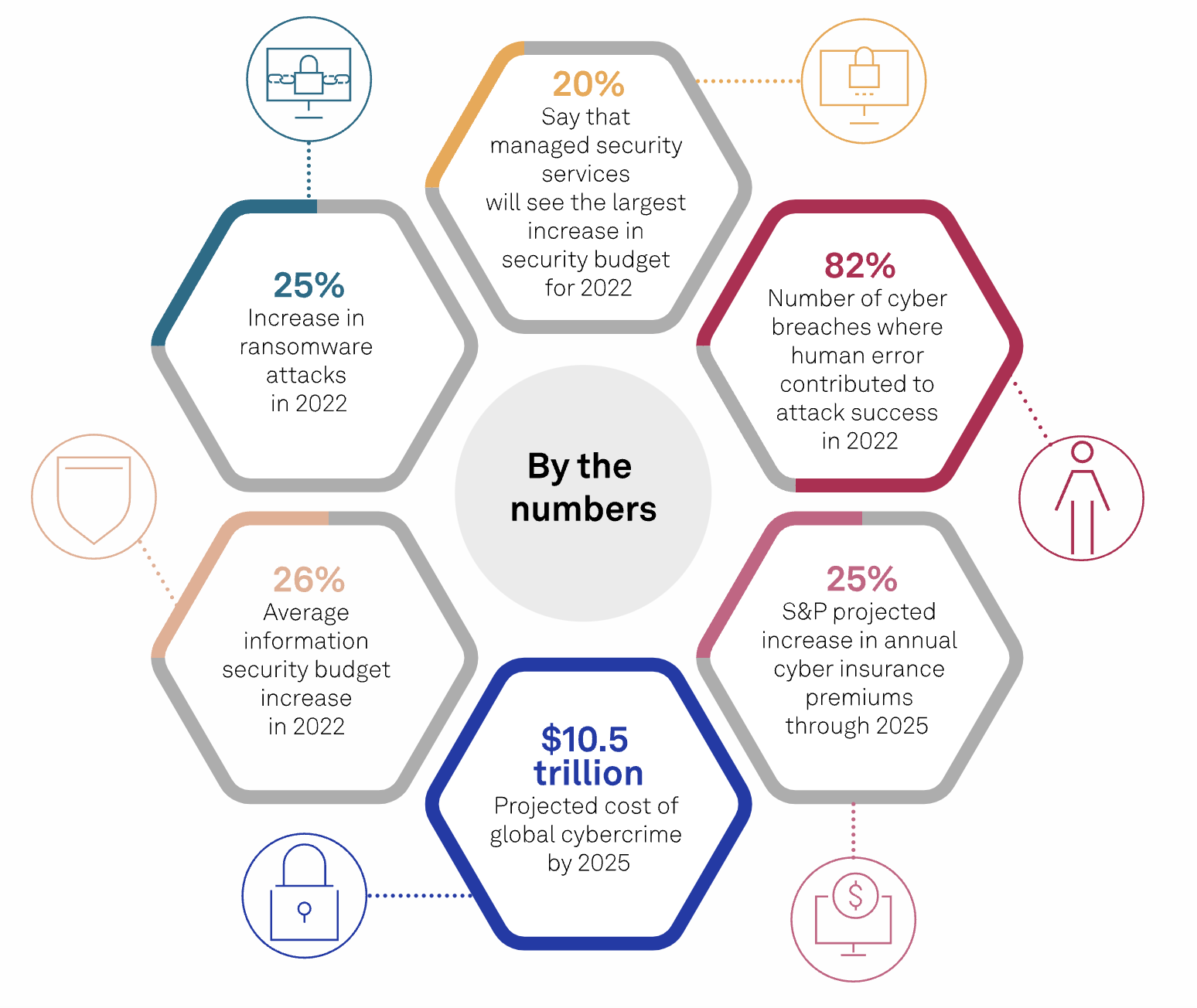
The global annual cost of cybercrime is estimated to be $6 trillion per year.
For instance, new cloud computing platforms have dramatically improved cyber threat detection thanks to the size and performance of their providers. This results in innovative breakthroughs in neural machine learning and analytics. In the poll Voice of the Enterprise: Information Security, Technology Roadmap 2022 conducted by 451 Research, respondents said they intended to “significantly increase” their expenditure on cyber security analytics. These advancements pave the way for more convenient methods of authentication for users of digital resources, such as facial recognition and other biometric processes.
Read 50 Key Points Of The Gartner Symposium, Spain 2023
Threats Are Changing
AI has several advantages and uses in many technology areas, including cybersecurity and data ops. AI and ML tools have become the quintessential ammunitions to track and take down cyber criminals and hackers, automate threat detection, and respond more efficiently than with traditional software-driven or manual methods.
Cybercrime up 600% Due to COVID-19 Pandemic
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are becoming increasingly valuable in IT security, assisting businesses in safeguarding their systems and data against advanced internet attacks. Predicting particular trends for 2024 is challenging, but here are some areas to keep an eye on in AI and ML within IT security: ML will be used to continually monitor and evaluate user behavior, devices, and network traffic for any deviations from the norm, as Zero Trust models continue to gain popularity.
Read: The Top AiThority Articles Of 2023
10 AI ML In IT Security Trends To Look Out For In 2024
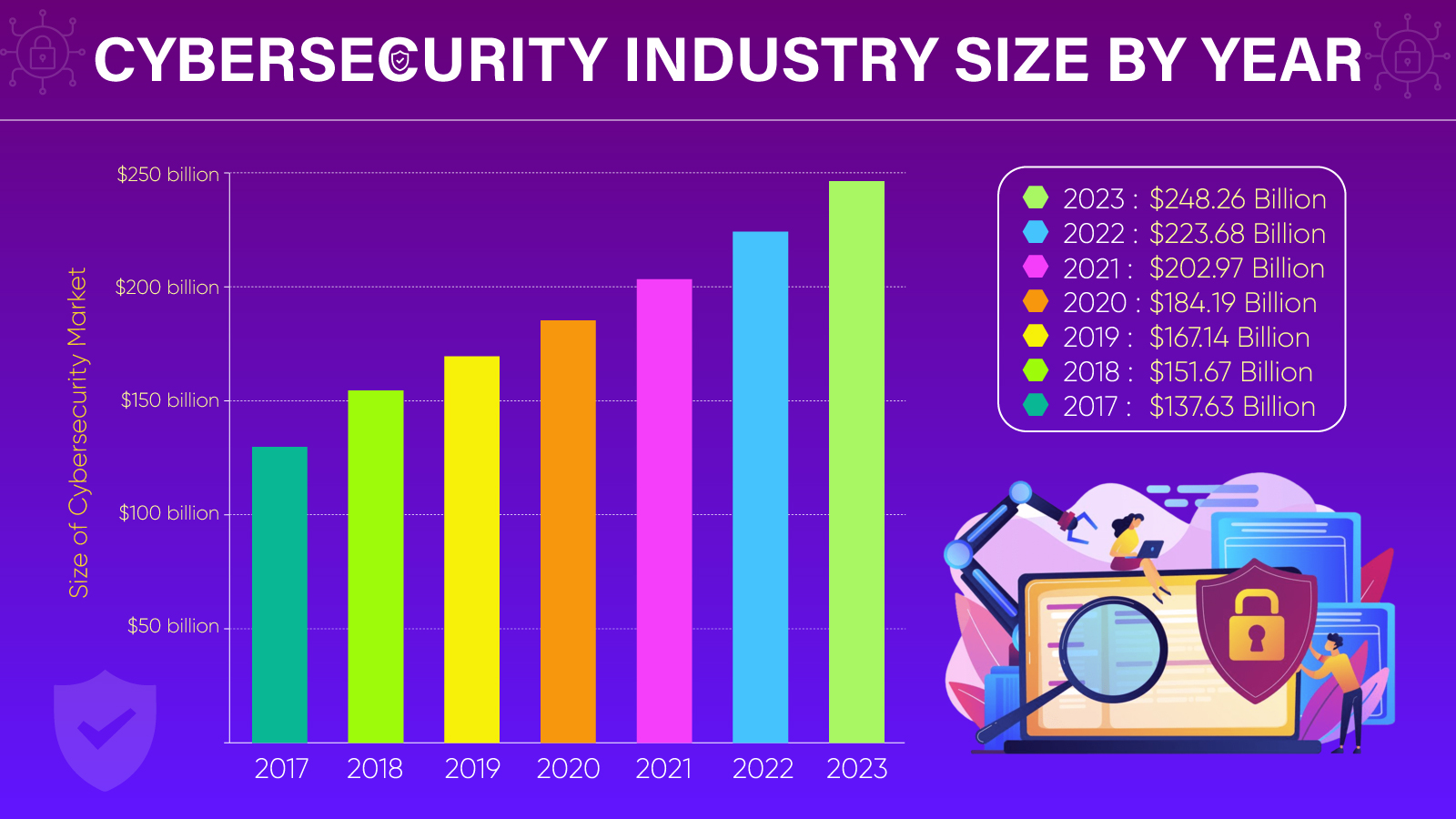 This graphic image has been taken from IBM for the year 2017-2023.
This graphic image has been taken from IBM for the year 2017-2023.
Zero Trust Security with ML: Zero Trust models will continue to gain traction, with ML being used to continuously monitor and analyze user behavior, devices, and network traffic for any deviations from the norm.
Let’s hear from Jasson Casey, Chief Executive Officer at Beyond Identity:
There is a high degree of urgency around zero trust today, especially when it comes to the first two pillars of the ZTMM – identity and devices. Research shows reusing stolen credentials and phishing remain the primary ways attackers access an organization to deploy ransomware, steal data, and access customer accounts. An increasing number of hackers are exploiting passwords and bypassing weak “legacy” multi-factor authentication (MFA), so strengthening an organization’s identity and device pillars right off the bat can make a substantial risk reduction difference.
AI-Enhanced Threat Detection: AI-driven threat detection will become more sophisticated, with systems capable of identifying even highly evasive and previously unknown threats by analyzing patterns and anomalies in network traffic and system behavior. Ransomware is an increasing menace despite being around for 20 years. Hackers have gotten skilled at disguising dangerous code, and there are over 120 ransomware families. Hackers can easily profit from ransomware, which explains its ascent. Another element was COVID-19. Many firms’ rapid digitalization and remote working made them ransomware targets. The number of attacks and demands rose.
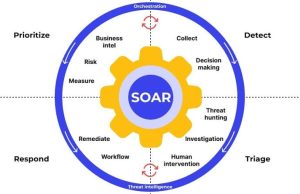 Security Automation and Orchestration: ML-driven automation will become a fundamental component of incident response, helping security teams rapidly analyze and respond to security incidents. Security automation and orchestration automate cybersecurity processes. Security procedures may be simplified and streamlined using automation. Security orchestration creates a process from security tools. Security automation simplifies and improves security operations by handling different types of routine tasks, while security orchestration integrates all of your security tools into a fast, efficient workflow.
Security Automation and Orchestration: ML-driven automation will become a fundamental component of incident response, helping security teams rapidly analyze and respond to security incidents. Security automation and orchestration automate cybersecurity processes. Security procedures may be simplified and streamlined using automation. Security orchestration creates a process from security tools. Security automation simplifies and improves security operations by handling different types of routine tasks, while security orchestration integrates all of your security tools into a fast, efficient workflow.
Predictive Threat Intelligence: ML will enhance threat intelligence by predicting potential threats based on historical data and global threat trends, allowing organizations to proactively defend against emerging cyberthreats. Cruise control, engine timing, door locks, airbags, and sophisticated driver support systems are connected by automatic software in modern automobiles. Bluetooth and WiFi allow these cars to interact, making them vulnerable to hackers. More autonomous cars are predicted to increase vehicle control and eavesdropping microphone use in 2023. Autonomous cars have a more complicated process that demands strong cybersecurity.
Cloud Security: AI and ML will continue to be deployed in cloud security solutions to monitor cloud infrastructure, detect misconfigurations, and defend against cloud-specific threats. Cloud vulnerability is a major cyber security trend. After the pandemic, remote working became common, increasing the need for cloud-based services and infrastructure and posing security risks to enterprises. Cloud services are scalable, efficient, and cost-effective. They are also key targets for attackers. Cloud misconfigurations cause data breaches, illegal access, insecure interfaces, and account hijacking. Organizations must reduce cloud dangers since data breaches cost $3.86 million on an average.
Deepfake Detection: With the rise of deepfake technology, AI and ML will play a critical role in detecting and mitigating the risks associated with deepfake content, particularly in sensitive areas like video authentication and voice recognition. Extended Detection and Response (XDR) is a vendor-specific SaaS threat detection and incident response technology that natively connects several security products. This modern cyber security plan usually includes prevention, detection, response, and recovery for new cyber threats. XDR models reduce reaction times to spot risks, automate forensic investigation, and duplicate data online for faster access. XDR bundles cyber security products utilizing a SaaS to gather and correlate advanced threat data, evaluate, prioritize, hunt, and remediate attacks to avoid security breaches. The targeted targeting and prevention of breaches by XDR reduces threat reaction time and offers unified insight across numerous attack channels.
Explainable AI (XAI): Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) helps humans understand and trust machine learning algorithm output. Explainable AI describes AI models, their effects, and biases. As AI models are increasingly integrated into security, there will be a growing need for transparency and explainability, ensuring that security professionals can understand why a particular decision was made by an AI system.
Adaptive Access Control: ML algorithms will be used to dynamically adjust access control policies, granting or denying access based on real-time risk assessments. According to IBM’s annual Cost of a Data Breach Report, breaches cost more and have more effect than before. All sectors’ average data breach cost is $4.3 million, up 13% in two years. The healthcare business has had the highest breach cost for 12 years, at a little over $10 million.
AI-Enhanced Security Awareness Training: ML algorithms will help organizations tailor security awareness training for employees, identifying areas of weakness and delivering personalized training to improve overall cybersecurity hygiene.
These trends reflect the growing importance of AI and ML in IT security, as the threat landscape continues to evolve. Organizations must stay updated on these trends and invest in the latest security technologies to protect their systems and data effectively. Additionally, compliance with relevant regulations and industry best practices should remain a top priority in IT security.
Behavior-Based Authentication: ML will be used for continuous user authentication based on behavior patterns, making it more challenging for attackers to gain unauthorized access. We all know that insecure passwords may let fraudsters access bank accounts, credit cards, and personal websites. This lets them steal your money, personal data, and digital security. Okta, an identity and access management business, reports that over 55% of organizations utilize MFA for security, rising annually. Look for more customers to use multi-factor authentication (MFA) in 2023 to make account hacking twice as difficult.
Read Top 20 Uses of Artificial Intelligence In Cloud Computing For 2024
Conclusion
The benefits of AI in cybersecurity outlined above are only the tip of the iceberg. The use of AI in this area is promising, but it is not without its drawbacks. Companies should devote far more time, energy, and money to developing and maintaining an AI system. In addition, you’ll need to collect a large volume of unique sets of malware codes, non-malicious codes, and abnormalities because AI systems are educated by utilizing data sets. Acquiring these data sets is time-intensive and demands expenses that most firms cannot afford.
Artificial intelligence systems can make mistakes or produce false positives if they don’t have access to massive amounts of data and events. Inaccurate information from questionable sources might have unintended consequences. The third issue is that there is a significant drawback in that fraudsters may utilize AI to evaluate their virus and conduct more sophisticated attacks. Artificial intelligence is quickly becoming an essential tool for improving the efficiency of IT security teams. It is beyond human capabilities to pose as an omnipresent doorman against newer cyberattacks, such as ransomware and social engineering. Human admins can’t act and respond against enterprise-level surface attacks without AI and predictive monitoring tools. The new-age AI for IT platforms delivers granular-level risk analysis and threat detection to empower security professionals. Together, human intelligence augmented by AI can decrease data risk with an improved security posture at all times.
Read OpenAI Open-Source ASR Model Launched- Whisper 3
[To share your insights with us, please write to sghosh@martechseries.com]

Comments are closed.