How we built GT Protocol’s AI Assistant
With the rapid advancement of AI technology, companies are now incorporating conversational AI into operations to work more efficiently and communicate better with customers. Training an AI model has become a major concern for success with any AI assistant. We created a detailed comparison of the top artificial intelligence platforms: Google Vertex AI, IBM Watsonx Assistant, and Microsoft AI Builder by reviewing their features, capabilities, and limitations, and further assess the various ways they contribute to shaping AI assistants.
Also Read: AI helps Data Engineers be Distinguished Data Engineers
1. Google Vertex AI Conversation –
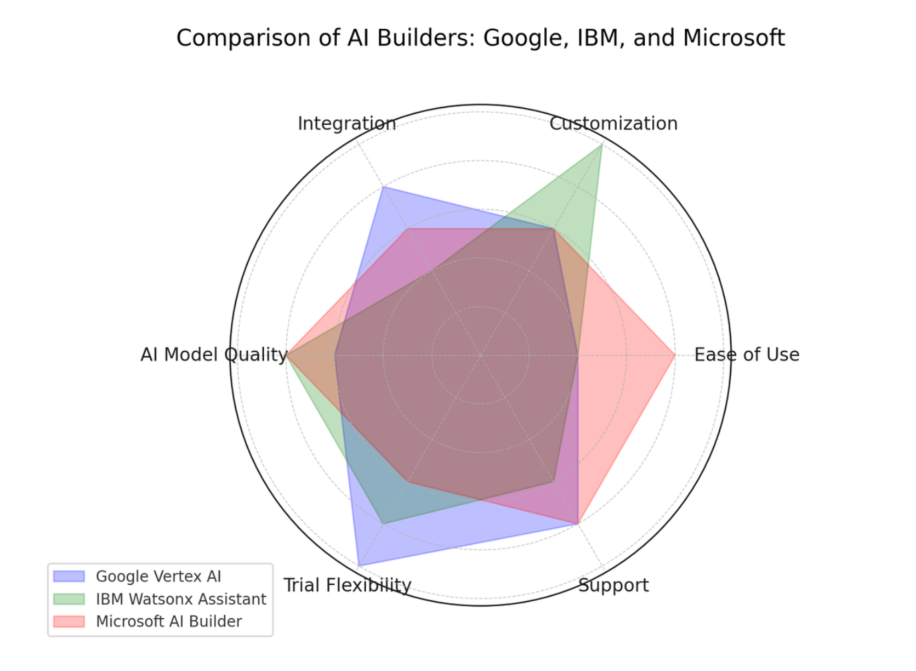
Google’s cloud-based platform is aimed for developing and deploying conversational AI models. Its power lies in an integral connection with the extensive infrastructure provided by Google, enabling robust data processing and AI functionality. Vertex AI provides users with the ability to integrate multiple agents and tools using a flexible command system, thus enhancing modularity and the scalability of the functionalities of an AI assistant.
Google provides an all-rounded monitoring system through which every business can monitor AI responses and performance in real-time, and the message flows.
Also Read: AiThority Interview with Rev Lebaredian, VP of Omniverse and Simulation Technology at NVIDIA
Vertex can integrate third-party systems such as CoinMarketCap, Telegram bots for value addition, and Soul Machines for making AI Avatars customer-facing.
Key Strengths
Best for native integrations with third-party tools and real time monitoring.
Limitations and Challenges
Outdated Language Models: The service currently makes use of Gemini 1.0 Pro, one of the older models, which limits how much context and naturalness complex conversations can have. The setup for the bots and training data is not very intuitive; it can be tough to deploy for first-timers.
Limited Tool Availability: While touting integrations with several tools, only the code interpreter is available, thus limiting its full potential for niche business needs.
Improvement Opportunities
This can be achieved through the complete integration of more advanced language models and smoothing the interface even further. Expanding the number of functionalities on the platform beyond a simple code interpreter would go a long way in making it even more useful for a wide variety of industries.
2. IBM Watsonx Assistant
IBM Watsonx Assistant is a prominent and powerful conversational AI with specific tuning for business process automation. It requires some training to operate it well but once you do, it performs excellently with complicated situation management in conversations.Advanced users can also access substantial options for customization, especially regarding dealing with variant conversational scenarios.
Key Strengths
Suited for the requirement of higher degree of customizations, complex conversation handling
Limitations and Challenges
- Complex Bot Training: Training bots in Watsonx Assistant requires a very high level of technical experience; hence, deployment would be slowed for those businesses that lack AI teams.
- Limitation of Integration Capabilities: Unlike Google’s platform, Watsonx does not easily integrate with popular messaging apps such as Telegram, reducing flexibility for automation in customer service.
- UI/UX Issues: The interface of the platform is complicated, hence difficult for beginners to get through and set up.
Avenues for Further Improvement
IBM can further develop Watsonx Assistant by making the process of training bots easier and developing more options for integration with external APIs. Enhancement in UI/UX would further open it up to businesses that do not have specific data science teams working on the platform.
3. Microsoft AI Builder
Microsoft’s builder is fully integrated with Microsoft Power Platform that allows companies to build AI models with little to no code experience. It focuses on automation within the Microsoft ecosystem. The AI Builder provides pre-built models of capabilities like form processing and object detection, with the provision for customization to allow businesses of any caliber the ability to access them. The tool easily integrates with Microsoft Power Apps, Power Automate, and Dataverse, thus enabling the automation of workflows without altering existing systems. The AI Builder has a non-technical, user-friendly interface that allows users to develop AI with ease.
Key Strengths
Ideal for those organizations whose requirements include low-code/no-code solutions integrated with Microsoft tools.
Limitations and Challenges
Limited to Microsoft Ecosystem: While the integrations with Microsoft tools are one of the high points, this does make the tool-less flexible for companies reliant on other platforms.
Advanced Customization Requires Expertise: While user-friendly, highly customized AI models may still require some basic understanding of AI concepts.
Avenues for Improvement
Microsoft could further this ability to use by extending support for integrations that fall outside of the core Microsoft ecosystem and offering higher degrees of customizations without requiring an end user to have deep technical knowledge.
Radar chart
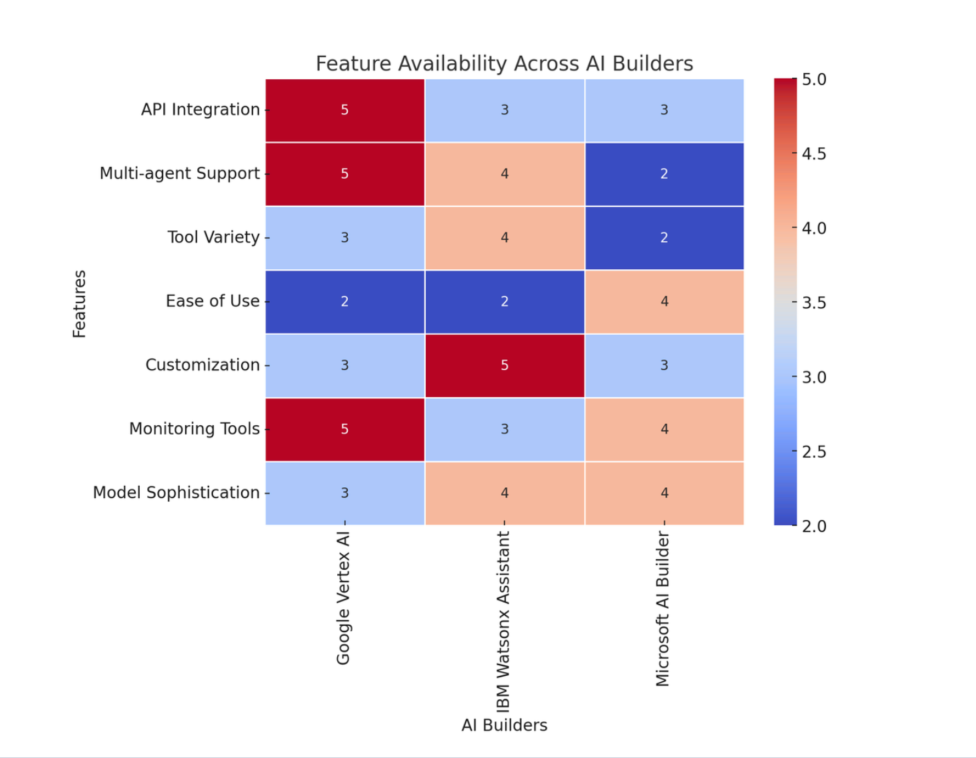 Heat map
Heat map
The choice of which AI builder is most applicable for specific business needs will be strictly based on those needs for each AI assistant that’s being built. The most important considerations to keep in mind are integration abilities, simplicity, scalability, and customization of models based on your business needs. Considering human resources and the availability of data scientists, some platforms have been designed for non-experts; therefore, businesses can perform the training of AI models themselves, without having an actual data science team.
Also Read: Real-Time Collaboration Between AI Agents: The Future of Autonomous Decision-Making in Business
[To share your insights with us as part of editorial or sponsored content, please write to psen@itechseries.com]

Comments are closed.