Decoding the Grid: A Practical Guide to Generative AI for Utilities
33 percent of utility and energy companies worldwide have begun to pilot generative AI and almost 40 percent of utility and energy companies have established a dedicated team and budget for generative AI.
After several false starts over many decades, artificial intelligence (AI) has finally proven its worth in helping people achieve faster results and with greater success. Even utilities, which are generally conservative in adopting new technologies, are thoughtfully embracing AI to improve customer experience, operational efficiencies, and infrastructure planning through smarter grid management.
Imagine knowing exactly how much energy is consumed inside every home or business, down to the individual appliance and time of day.
Would your utility’s business managers be able to operate and plan grid infrastructure more efficiently?
Now, imagine knowing what type of appliance each home was using. Would your utility’s marketing team be able to target gas furnace customers for electric heat pump upgrades more accurately and cost-effectively, for example?
The capabilities of today’s AI algorithms are helping utilities do just this by illustrating with precise detail how energy moves along the grid. In just a few clicks, utilities can identify key power loads – including electric vehicle (EV) charging, solar, batteries, HVAC, and water heaters – detect behavior and appliance inefficiencies, track consumption history, filter consumption patterns by geography, income level, and more.
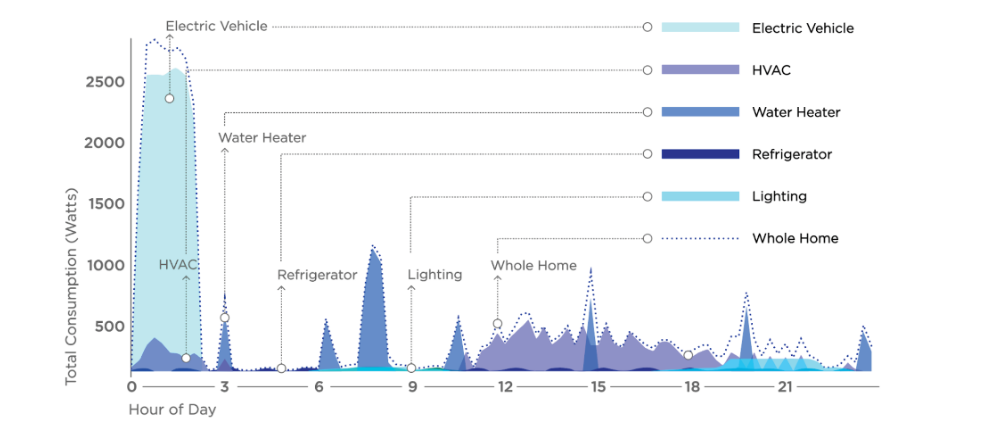 For the first time, utilities can draw meaningful insights from consumption data that lend to smarter decision-making for critical initiatives like time-of-use (TOU) load shifting, distribution planning, and demand-side management.
For the first time, utilities can draw meaningful insights from consumption data that lend to smarter decision-making for critical initiatives like time-of-use (TOU) load shifting, distribution planning, and demand-side management.
A Trusted ‘Knowledge’ Repository is Key to Generative AI Adoption in 2024
New in the Evolution of AI
While AI has slowly been developing since the 1940s – and large breakthroughs in the first few decades brought us ELIZA, the first chatbot – it wasn’t until 2011 that the ‘smartness’ of AI started to pick up. Apple integrated Siri into its iPhones, IBM Watson won Jeopardy, and Google’s AlphaGo won the World Go Championship. All of a sudden, AI was on the map for tech and non-tech companies everywhere.
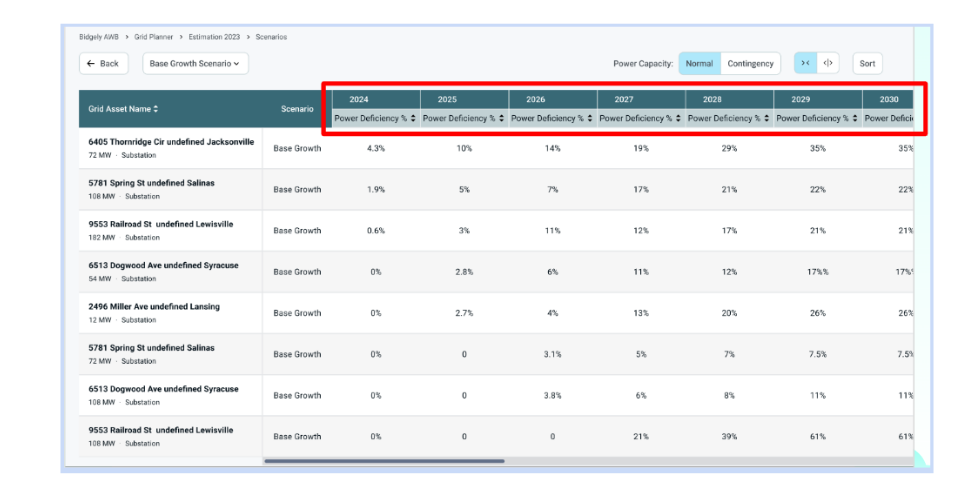
Current AI capabilities – which are considered ‘traditional AI’ – are being used in the utility world to connect what is happening on the grid with how utilities carry out top-level decision-making and day-to-day activities. For example, using AI to analyze power consumption on an hour-by-hour basis, network planners can optimize grid management by running capacity analysis on transformers, feeders, and substations. This enables them to identify areas of the grid that are being overloaded and which areas are capable of withstanding an increase in demand.
 Another typical use is taking AI’s ability to detect appliance-level consumption patterns within each home to personalize customer communications that encourage behavioral energy efficiency. Specifically, utilities can send out usage alerts as a house comes close to crossing the high-bill threshold.
Another typical use is taking AI’s ability to detect appliance-level consumption patterns within each home to personalize customer communications that encourage behavioral energy efficiency. Specifically, utilities can send out usage alerts as a house comes close to crossing the high-bill threshold.
Because, AI can draw side-by-side comparisons of homes based on energy consumption, property attributes, individual lifestyles, and geography, utilities are also better positioned to establish benchmarks for initiatives like electrification and demand response. Some utilities are even using these AI-powered consumption insights to identify and prevent meter tampering and tariff misuse.
But the world is entering a new era with generative AI, which promises to be even more powerful.
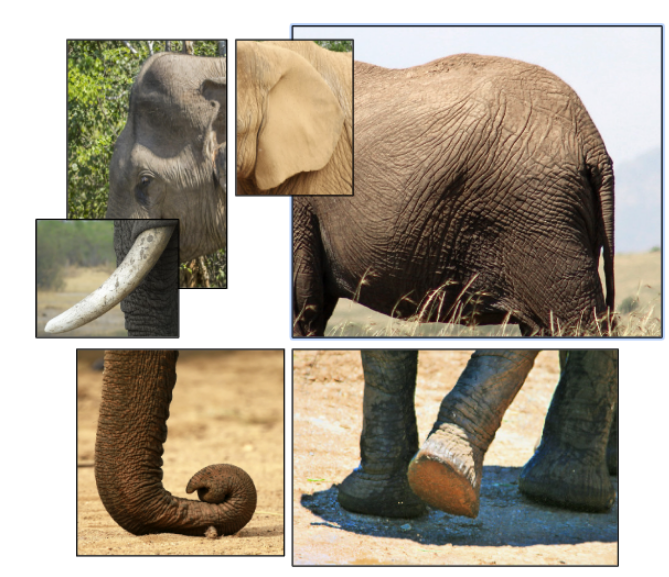
When traditional AI algorithms see a picture of an elephant, they process the elephant as a whole and can describe it in intricate detail, capturing every pixel. When asked to draw the elephant, traditional AI algorithms will draw that elephant in nearly the same way again and again.
Generative AI, however, is more creative. These ML algorithms instead capture key features of the elephant to draw a different elephant each time.
 This evolution brings incremental creativity to the problems around us – the type of creativity most of us have to apply on a day-to-day basis – and allows organizations to enhance operations from the top down without drastic restructuring of business models.
This evolution brings incremental creativity to the problems around us – the type of creativity most of us have to apply on a day-to-day basis – and allows organizations to enhance operations from the top down without drastic restructuring of business models.
Although generative AI is still in its infancy in regards to scaled adoption and implementation, recent research from Capgemini Research Institute revealed that 33 percent of utility and energy companies worldwide have begun to pilot generative AI and almost 40 percent of utility and energy companies have established a dedicated team and budget for generative AI.
While Capgemini notes high-tech and industrial manufacturing as the two industries at the forefront of generative AI, it is perhaps more interesting to see industries notoriously slower to adopt technological innovations (like utilities) are supporting generative AI at the same pace as its tech-savvy counterparts.
Generative AI for Utilities
As impressive as Siri was when it was first introduced, generative AI is garnering that same admiration.
Generative Pre-trained Transformer 4 (GPT-4) passed the Bar Exam with flying colors, so it’s not difficult to imagine how applying this resource will continue to improve utility operations.
Traditional AI is incredibly valuable in analyzing data, which for utilities means appliance detection, consumption profiling, and everything that comes from this sophisticated energy intelligence like segmenting customers, sending automatic high-usage alerts, etc. With generative AI, utilities have the power to further amplify operations.
Implementation of generative AI within areas like call centers to reduce time spent on the phone with customers will be the most obvious and low-risk use of AI in the near term, it is also low-hanging fruit for most utilities. Where utilities will see the greatest impact overall, however, will be grid planning and management.
For instance, as utilities currently work to support rising EV adoption they rely on human input to determine their EV charging infrastructure strategy. This means planning when, where, and how many EV chargers to install at any given location. In the absence of much historical data (which is what traditional AI depends on), such a task requires significant amounts of creativity around human behavior as well as a firm understanding of how charging infrastructure is likely to affect EV purchases, demographic changes, and even real estate availability. This now is a task well suited to be tackled by generative AI.
Another great example is the use of generative AI chatbots by utility business managers, not just customers. Utility managers can interact with underlying big data in a natural language mode via initial questions such as, “Which five substations have the highest solar penetration?”
They can then dive deeper with follow-on questions such as:
“How many EV drivers are at this substation?”
“How many of those users have both solar and EVs?”
What are the time of use patterns for these users?”
With this, grid planners can easily identify areas of focus within minutes, rather than the weeks that it would have taken an analyst to download and analyze the data before answering these questions.
A Smarter Energy Future with Generative AI for Utilities
AI-powered consumption insights at this level can unlock considerable financial savings for utilities. EV load shifting can save utilities upwards of $1,350 per EV every year in bulk system investments and $1,090 per EV every year in distribution system investments – a financial benefit that compounds as adoption grows.
And, that’s just the beginning.
McKinsey Global Institute estimates AI and machine learning can drive $2.6 trillion to $4.4 trillion annually in business value. This could mean $200 billion in value add for the U.S. utility industry thanks to AI helping utilities avoid costly and unnecessary infrastructure upgrades, improving grid planning, reducing operating spending, and more.
While full-scale adoption of AI strategies may be decades away, the success of early pilot programs and projects proves there is no reason to wait. Utilities can start working more efficiently today – both in terms of employee workload and by uncovering new business opportunities – and build a stronger, more reliable grid.

Comments are closed.