Fujitsu and Delft University of Technology Collaborate to Establish Cutting-Edge Quantum Lab
Fujitsu and Delft University of Technology announced the establishment of the Fujitsu Advanced Computing Lab Delft at Delft University of Technology, an industry-academia collaboration hub dedicated to the development of quantum computing technologies. The new collaboration hub will be positioned as part of the Fujitsu Small Research Lab initiative, which dispatches Fujitsu researchers to technology incubators at leading global universities to conduct joint research with some of the top researchers in their fields, including professors as well as the next generation of innovators.
The Advanced Computing Lab will be established at world-leading quantum technology research institute QuTech – a collaboration between Delft University of Technology and the Netherlands Organization for Applied Scientific Research (TNO) – and aims to accelerate R&D of diamond-spin quantum computing, a technology that Fujitsu and Delft University of Technology have been jointly researching since October 2020.
In addition, the two partners will further advance the development of real-world quantum applications, and aim to realize innovative fluid simulation technologies that apply quantum computing to the field of computational fluid dynamics, where large-scale and complex computations represent an ongoing challenge.
Collaboration to focus on diamond-spin quantum technology
As part of efforts to strengthen collaboration with cutting-edge research institutions through global open innovation, Fujitsu has been conducting basic research and development into quantum computers using diamond-based spin qubits with TU Delft.
To date, the two partners have been conducting R&D on quantum computers using diamond-based spin qubits with the aim to create a blueprint for future modular quantum computers that can scale beyond 1,000 qubits. To make practical quantum computing a reality, Fujitsu and Delft University of Technology have been conducting research on associated technology layers, from the device level to control systems, architecture and algorithms. As a result, the two partners realized the world’s first fault-tolerant operation of spin qubits in a diamond quantum processor using the diamond NV center method.
Fujitsu and Delft University of Technology are further working to improve the performance of qubits by integrating SnV centers , which are gaining increasing attention as high-performance diamond spins, in scalable nanophotonic devices showing efficient single-photon coupling.
The two partners have established the Fujitsu Advanced Computing Lab Delft to further strengthen their cooperation and enhance the collaboration and research framework for the development of advanced computing technologies based on quantum technologies. Moving forward, Fujitsu and Delft University of Technology will position the new hub as a leading industry-academia research and development center in Japan and the Netherlands, and promote further collaboration including the development of talent that is able to lead th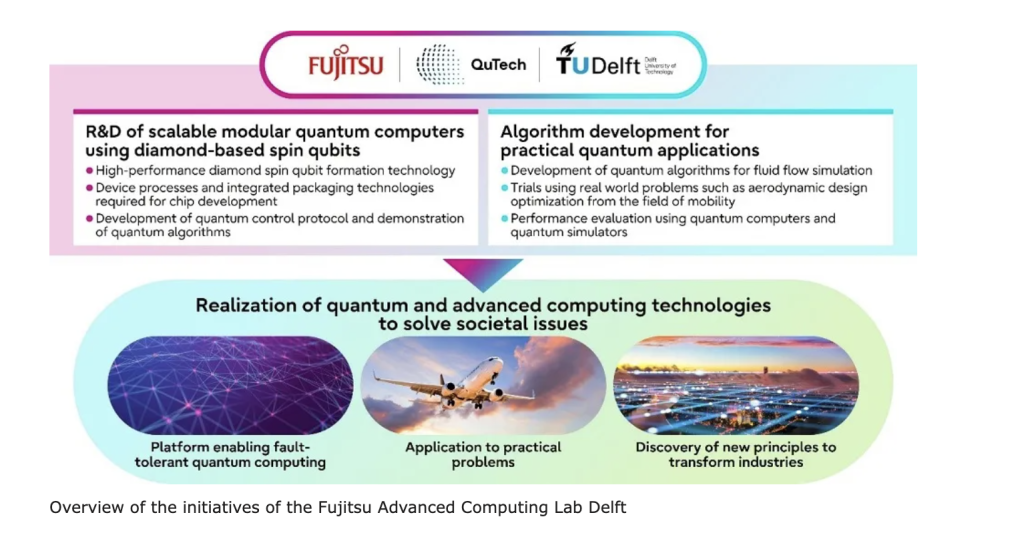 e development of solutions to societal issues using advanced computing technologies.
e development of solutions to societal issues using advanced computing technologies.
Read: State Of AI In 2024 In The Top 5 Industries
Breakthroughs beyond the results
[1] Fujitsu Small Research Lab :An initiative to achieve greater breakthroughs beyond the results of ordinary joint research. The initiative aims to contribute to the solution of social issues, while accelerating joint research, identifying new research themes, developing human resources, and building medium- to long-term relationships with universities. Fujitsu researchers are embedded at technology incubators at universities in Japan and internationally.
[2] QuTech :Formally established in 2015 by Delft University of Technology and the Netherlands Organization for Applied Scientific Research (TNO). QuTech’s mission is to develop a scalable prototype of a quantum computer and an inherently secure quantum Internet based on the fundamental laws of quantum mechanics.
[3] The world’s first fault-tolerant operation of spin qubits in a diamond quantum processor :“QuTech and Fujitsu realise the fault-tolerant operation of a qubit” (QuTech press release May 5, 2022): https://QuTech.nl/2022/05/05/QuTech-and-fujitsu-realise-fault-tolerant-operation-of-qubit/, Abobeih et al. (2022), “Fault-tolerant operation of a logical qubit in a diamond quantum processor,” Nature, DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04819-6
[4] Diamond NV Center :A defect consisting of a vacancy in the diamond lattice next to a nitrogen atom, where a carbon atom is typically found.
[5] SnV Center :A defect consisting of a vacancy in the diamond lattice next to a tin (Sn), where a carbon atom is typically found.
[6] FTQC :Abbreviation for fault-tolerant quantum computation; performance of quantum computation without errors while correcting quantum errors
[To share your insights with us as part of editorial or sponsored content, please write to sghosh@martechseries.com]

Comments are closed.