AI In XM: The Role of XM in Driving Business Success
Did you attend the recent XM event of Qualtrics in Salt Lake City? Well, that was an awesome event for the techies. If you missed the XM summit you can cover it here.
In this blog, we shall be discussing in-depth about Experience Management (XM) and its applications, benefits, and future trends.
Seventy-five percent of customers are willing to overlook the prices to buy from companies that offer a good customer experience- Zendesk
TOC
- What is Experience Management (XM)?
- The Six Laws of Experience Management
- What are the Benefits of XM?
- Industry Comments
- Applications of XM
- Practical Examples of XM
- Top XM Companies in 2024
- The Next Decade of XM
- The Role of XM in Driving Business Success
- Guide to CRM, CXM, UX, and EEM
- FAQ’s
What is Experience Management (XM)?
To create and enhance the experiences you offer, it is important to listen to the opinions of consumers, workers, and other stakeholders. This may be done comprehensively through the practice of Experience Management (XM). Businesses use it to create new experiences for their customers and employees based on insightful market research that reveals unfulfilled needs. They can then tweak and improve these experiences over time to meet the evolving demands of their market and stakeholders.
The goal of Experience Management is to create positive and memorable experiences for customers, employees, partners, and other stakeholders, ultimately leading to increased loyalty, satisfaction, and advocacy. By consistently delivering exceptional experiences, organizations can differentiate themselves from competitors and drive long-term success.
This image has been taken from the Qualtrics website.
In summary, XM is a strategic approach to understanding and improving all the experiences people have with an organization. By focusing on all these aspects, companies can create a more positive and sustainable business environment.
Read: Qualtrics Launches Three New AI-Powered Suites for CX, EX, and Research
Customer experience management is the management of customer interactions through each physical and digital touchpoint to deliver personalized experiences that drive brand loyalty and increase revenue, said David Clarke, global chief experience officer at PwC.
“The Six Laws of Experience Management,” which are:
-
- Journeys add meaning to moments
- Actions transform insights into value
- Commitment aligns behaviors
- Leaders boost or break inertia
- People are emotional, not rational
- XM is a habit, not an act.
What are the Benefits of XM?
The six XM Competencies—LEAD, REALIZE, ACTIVATE, ENLIGHTEN, RESPOND, and DISRUPT—that organizations should focus on to improve their XM capabilities. The image below has been taken from the Qualtrics website.
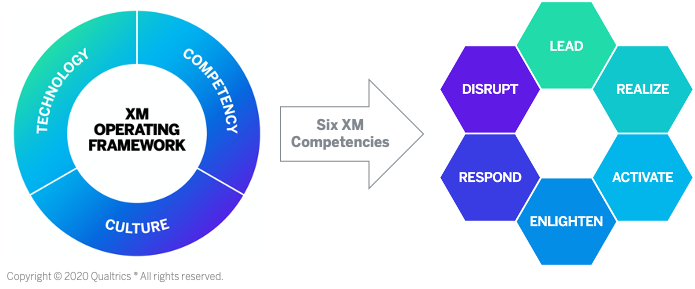
- Synthesize solicited and u********** brand feedback
- Customization
- Evaluate overall brand health
- Detect customer service weaknesses
- Identify how customer sentiment changes over time
- Provide automated and quick follow-up
- Interpret nuance in conversation to offer a more realistic sentiment analysis
- Operational Efficiency
- Reduced Churn and Negative Reviews
- Enhanced Customer Insights
- Increased Revenue
- Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty
Industry Comments
We have a guest post on AiThority by Brad Anderson, President of Product, User Experience, Engineering and Ecosystem, and Qualtrics Experience Management solutions.
Customers Are Tired Of Telling Businesses What To Do – They Want Businesses To Listen
Businesses wrestle with another challenge in 2025. They may have trouble even identifying broken customer experiences due to a growing reluctance from consumers to provide direct feedback to the companies they do business with. Qualtrics research found that since 2021, the share of consumers providing feedback directly to the companies they buy from following a very bad experience has fallen by 7.2 percentage points.
Leaders in 2024 must have a plan in place to listen to indirect feedback, things like call center conversations, online chats, and social media posts. The smart harnessing of AI can enable companies to capture and analyze this indirect feedback and construct a rich insight into customer expectations, even capturing data points that might never appear in a customer satisfaction survey.
With so much spending at stake in 2024, companies need to prioritize delivering superior customer experiences that fuel loyalty and drive sustained growth. Businesses that fail to recognize the current market dynamics risk losing long-term customers to their competitors.
The future is about Human Intelligence accelerated and scaled with Artificial Intelligence. Invest wisely in your frontline employees and harness technology judiciously to strike the right balance between AI and human interaction.
Applications of Experience Management (XM)
The image below has been taken from the Qualtrics website.
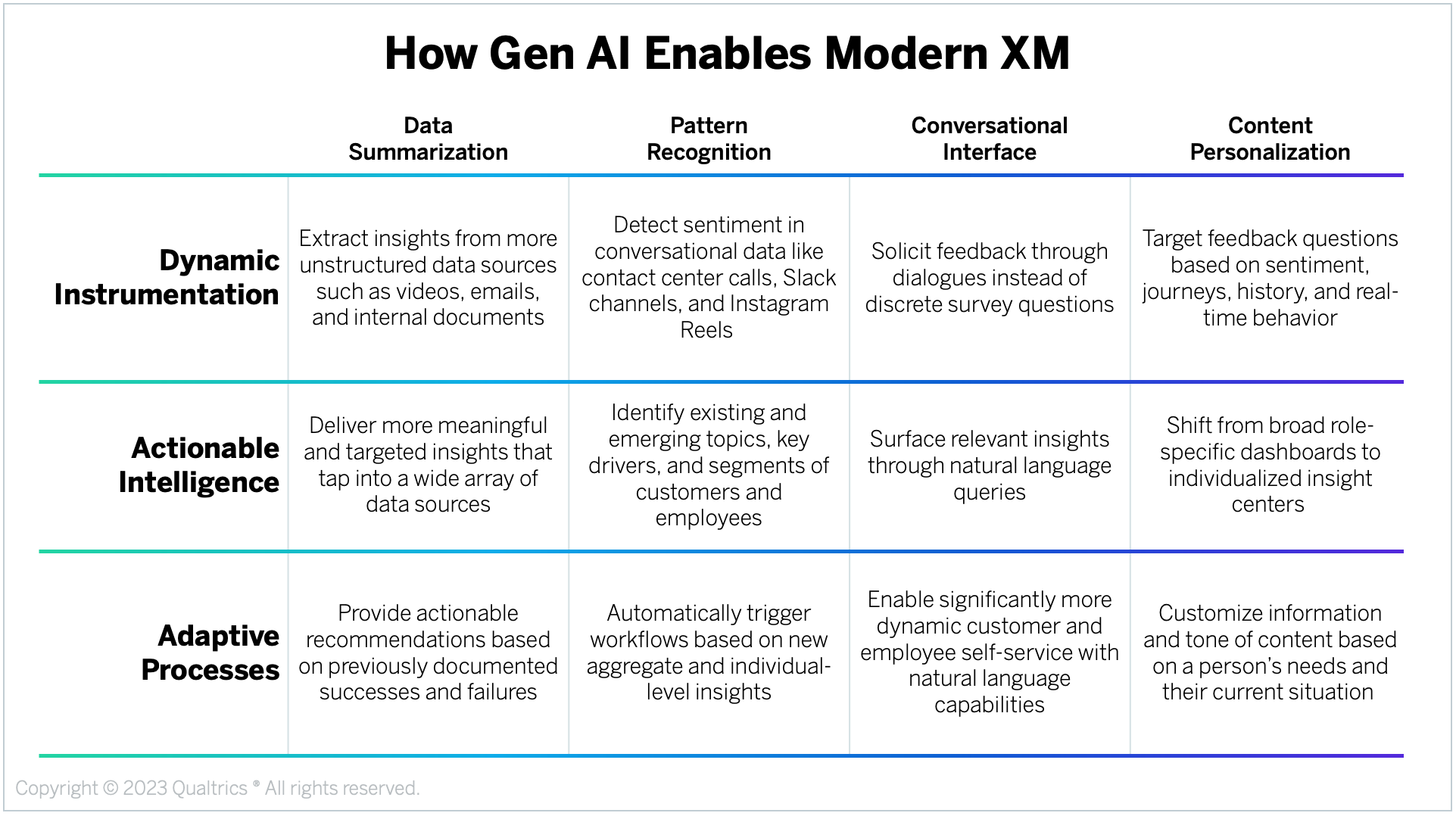
-
Customer Experience (CX): This is perhaps the most well-known application of XM. By collecting feedback and data on customer interactions (surveys, reviews, social media), companies can understand customer needs and pain points. This allows them to improve touchpoints throughout the customer journey, leading to higher satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy.
-
Employee Experience (EX): XM can also be used to focus on employee satisfaction and engagement. By gathering feedback from employees through surveys, focus groups, or exit interviews, companies can identify areas for improvement in areas like work environment, compensation, and professional development. Engaged employees are more productive, stay with the company longer, and deliver better customer service.
-
Product Development: XM can inform product development by incorporating customer feedback into the design process. Companies can use surveys and user testing to understand customer preferences and identify unmet needs. This can lead to the development of products that are more user-friendly and meet customer expectations.
-
Brand Management: XM can help companies build a strong brand image. By understanding how customers perceive the brand, companies can identify areas where the brand message is not resonating. XM can also be used to track brand sentiment on social media and address any negative perceptions quickly.
- Market Research and Insights: XM tools and methodologies provide valuable insights into market trends, consumer behavior, and competitor activities. By continuously gathering feedback and analyzing data, organizations can stay ahead of market changes and make data-driven decisions.
- Operational Excellence: XM can also be applied to improve operational processes and efficiencies. By gathering feedback from employees and customers on operational workflows, organizations can identify areas for improvement, streamline processes, and reduce costs.
- Risk Management: XM helps organizations identify and mitigate potential risks by monitoring customer and employee feedback for signs of dissatisfaction, disengagement, or other issues. Proactively addressing these concerns can help prevent larger problems from arising.
- Crisis Management and Recovery: During times of crisis, such as a product recall or a public relations issue, XM enables organizations to quickly gather feedback, assess the impact on stakeholders, and develop appropriate responses to mitigate damage to the brand and rebuild trust.
- Partner and Supplier Relationships: XM extends beyond the organization to include partners and suppliers. By gathering feedback from these stakeholders, organizations can strengthen relationships, address any issues, and foster collaboration for mutual benefit.
- Continuous Improvement Culture: Ultimately, XM promotes a culture of continuous improvement within organizations, where feedback is valued, and actions are taken to address issues and drive positive change across all aspects of the business.
-
Other Stakeholders: While Customer and Employee experience are the most common applications, XM can be applied to understand the experience of other stakeholders like suppliers or partners. This can help build stronger relationships and improve overall business performance.
Practical Examples of Experience Management (XM)
1. When you buy something online and get an email asking how your experience was, that’s Experience Management.
2. If you tell a company what you think about their service and they make changes based on your feedback, that’s Experience Management.
3. When you walk into a store and see smiley faces or buttons to press to rate your experience, that’s Experience Management.
4. If you visit a website and it remembers your preferences, like your language or favorite items, that’s Experience Management.
5. When a company quickly solves your problem after you complain, that’s Experience Management.
6. If you get training at work to help you do your job better and make customers happier, that’s Experience Management.
7. When you use an app that’s easy to understand and use because the company listened to feedback from users, that’s Experience Management.
8. If you call customer service and the person on the phone is friendly and helpful, that’s Experience Management.
9. When a store is clean, organized, and easy to find things in, that’s Experience Management.
10. If a company makes a new product because customers asked for it, that’s Experience Management.
Top XM Companies in 2024
The Role of XM in Driving Business Success
Data is essential for us to enhance the experiences we offer. This, however, is not the sole justification for tracking and enhancing them. Even for market leaders, experience management is critical due to the universal truth that consumers purchase experiences rather than physical goods.
Most of the time, when a client or customer is unhappy, we assume it’s because the service or product failed to meet their expectations. We investigate potential production and quality control issues, or we review our key performance indicators to determine if we achieved our objectives. But it’s rarely the product’s quality that causes consumers to switch brands. They decide to switch after a bad experience. A beautifully made washing machine, for instance, won’t mean anything to a buyer who can’t decipher the icons on the screen.
There is value in experience as well. Not because they can afford to, but because the moment a consumer opens the box is the best chance to make them fall in love with the goods inside, companies like Tiffany & Co. and Apple invest in memorable packaging. Customers are less likely to be disappointed if the goods don’t live up to their expectations if the brand manages to evoke positive emotions during the buying process. Satisfied customers might become brand champions after having a great experience. The difference between a well-designed product or service that meets a one-time need and one that inspires loyalty over time is the quality of the experience.
Guide to CRM, CXM, UX, and EEM
- From the point of view of the business, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) entails handling customer data. Some examples of such metrics to track are the volume of support tickets and phone calls.
- Managing data from the customer’s point of view is the focus of Customer Experience Management (CXM or CEM). Customer Experience Management seeks to identify the initial reason someone sought assistance rather than just counting the number of calls. Although they approach the problem from different angles, both have a common goal: consumer satisfaction.
- Another popular alternative is user experience, which can be referred to as UX, UX Design, or UX Research. Designing digital products and digital consumer experiences is the primary emphasis of this subfield of Experience Management.
- Every human resources department must have an employee experience management (EEM) strategy. But the language has changed because we no longer view workers as commodities to be used for profit. As a result, “Human Capital Management” became the new HR term.
FAQ’s
- What are the key components of Experience Management? The key components of XM include understanding the needs and expectations of stakeholders, measuring experiences through feedback and data, analyzing insights, taking action to improve experiences, and continuously iterating and optimizing.
- What are some common methods for measuring experiences? Common methods for measuring experiences include surveys, interviews, focus groups, customer feedback tools, sentiment analysis, Net Promoter Score (NPS), Customer Satisfaction (CSAT), and Employee Satisfaction (ESAT) surveys.
- How does Experience Management differ from Customer Experience (CX) or Employee Experience (EX)? Experience Management (XM) encompasses both Customer Experience (CX) and Employee Experience (EX), along with other stakeholder experiences. CX focuses on the experiences of customers, while EX focuses on the experiences of employees.
- What are some benefits of implementing Experience Management in an organization? Benefits of XM include increased customer satisfaction and loyalty, higher employee engagement and retention, improved product and service quality, better decision-making based on insights, and competitive advantage.
- How can organizations collect feedback to improve experiences? Organizations can collect feedback through various channels, including surveys, social media monitoring, online reviews, suggestion boxes, focus groups, and direct interactions with customers and employees.
- How can organizations use Experience Management to drive innovation? By listening to customer and employee feedback, identifying pain points and unmet needs, and experimenting with new ideas and solutions, organizations can innovate and differentiate themselves in the market.
- What role does leadership play in fostering a culture of Experience Management? Leadership plays a critical role in setting the vision, values, and priorities for XM, allocating resources, empowering employees, leading by example, and championing the importance of delivering exceptional experiences at every level of the organization.
- How can organizations ensure that they are delivering consistent experiences across different touchpoints? Organizations can ensure consistency by mapping the customer journey or employee journey, identifying key touchpoints, standardizing processes and interactions, training employees, and using technology to monitor and enforce standards.
- What are some common challenges faced when implementing Experience Management initiatives? Common challenges include siloed data and departments, resistance to change, lack of leadership buy-in, difficulty measuring ROI, managing large volumes of feedback, and maintaining momentum over time.
The Next Decade of XM
So, how can you know if you’re making progress with your XM initiatives? Having a well-defined goal in mind is essential for tracking your progress. The image below has been taken from the Qualtrics website.
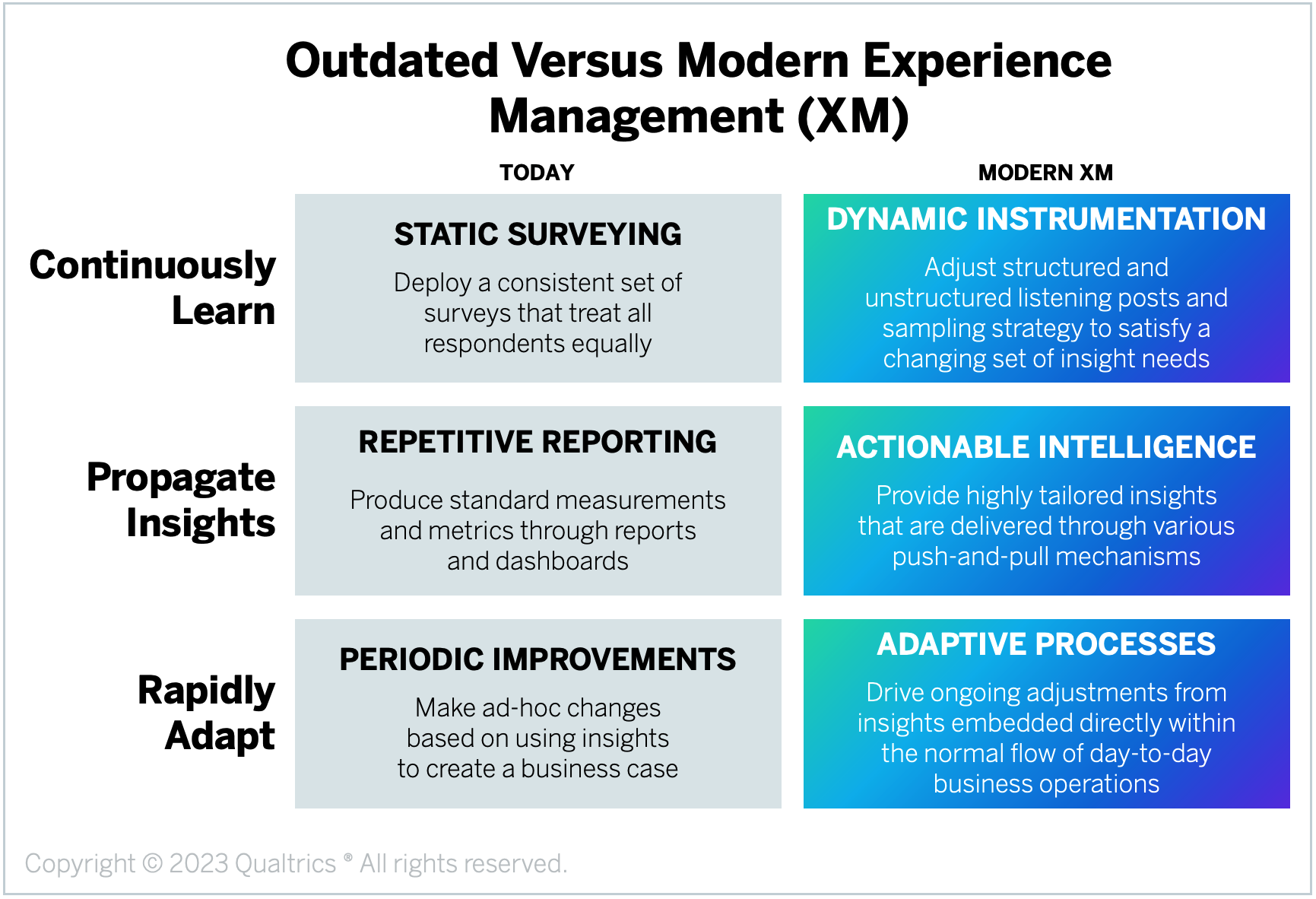


Comments are closed.